How Industry 4.0 Is Transforming Manufacturing in Canada
Over two-thirds of Canadian manufacturers agree that digital transformation is crucial for their talent and customer strategies. And Canada’s manufacturing industry players are racing to stay competitive. Over two-thirds of them are investing in cloud, data capturing, ERP, robotics and automation, and advanced analytics.
These and other digital technologies are to Industry 4.0 what steam power was to the first industrial revolution. They’re driving unprecedented productivity and efficiency gains, cost savings, and product quality increases – to name just a few.
Here’s everything you need to know about Industry 4.0’s role in manufacturing in Canada, from drivers for adoption and examples to benefits, solutions, and implementation steps.
The State of Canada’s Manufacturing Industry
Manufacturing retains its key place in the Canadian economy: the industry still accounts for roughly 10% of its GDP. It’s also responsible for 60% of Canada’s exported goods.
Despite the supply chain disruptions and turbulent demand brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic, Canadian manufacturers are optimistic about their prospects.
Three-quarters of manufacturers expect their revenue to increase by 2.5% and 9.9% within the following three years. They also plan to increase their headcount by up to 10%. Their optimism is fueled by rising global demand, favorable government policies, increasing investments, and, of course, technological advancements.
Of course, that doesn’t mean Canada’s manufacturing industry isn’t facing certain challenges, such as:
Potential economic decline. Almost a fifth – 18% – of surveyed Canadian manufacturers are worried about rising interest rates and inflation.
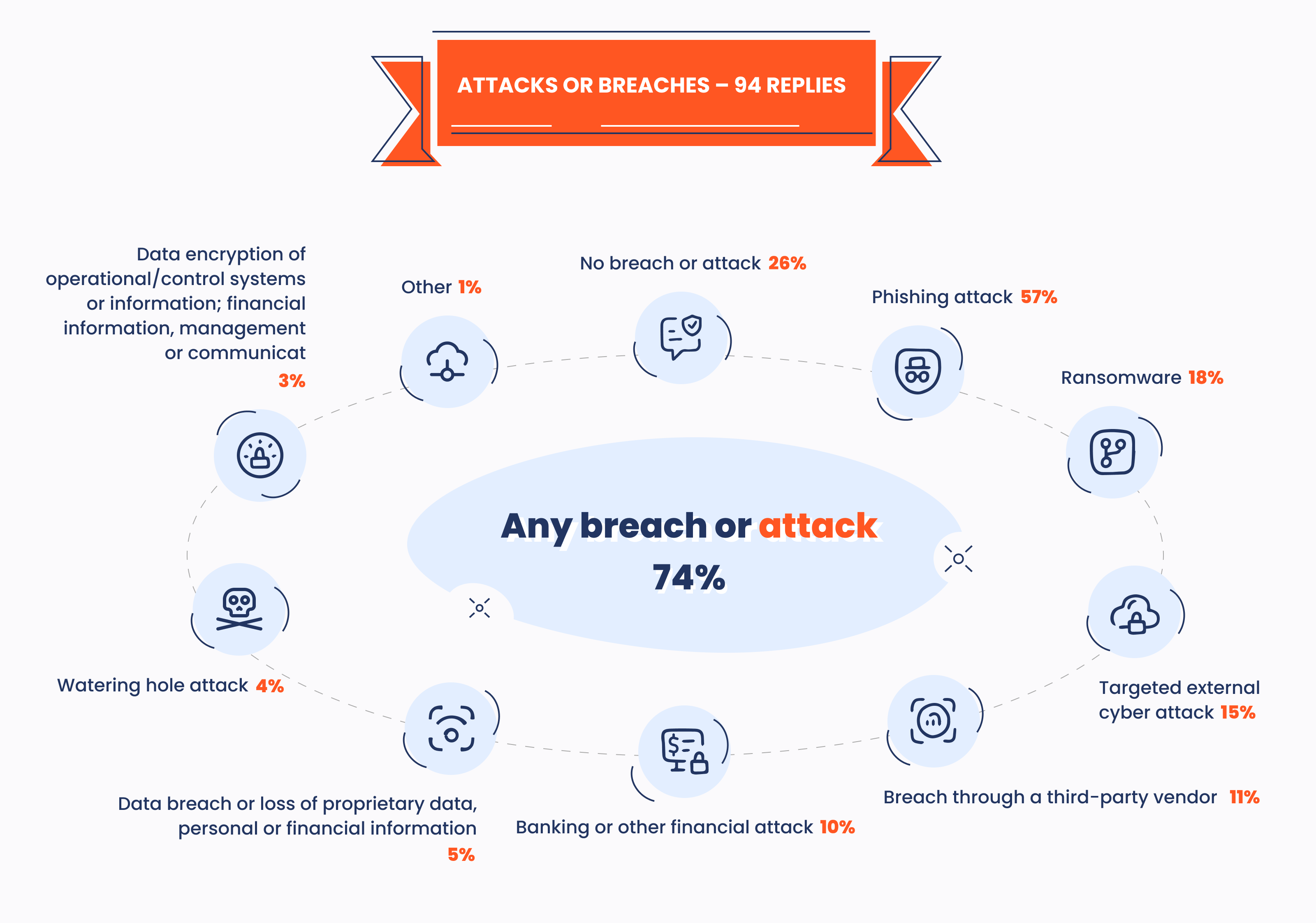
Cybersecurity. 76% of Canadian manufacturers are highly concerned about their systems’ security. The share of manufacturers that have experienced a cyberattack also jumped up from 74% in 2024 to 56% in 2023.
Talent shortages. Although the number of unfilled positions has been going down since its peak in 2022, talent shortages are from over. That’s why manufacturers continue to experience disruptions due to competing for talent – and cite lack of available talent as a key challenge.
Climate change risks. CxOs worldwide are calling climate change a top-three issue, and Canada is no exception. Addressing this challenge requires careful consideration of risks across the board, from waste management to software development sustainability.
3 Key Drivers Behind Industry 4.0 Adoption
There are three key reasons why Canadian manufacturers turn to Industry 4.0 solutions:
Favorable government policy. The Canadian government has taken several steps to encourage advanced manufacturing, with the creation of Innovation Clusters being the most notable one.
Economic factors. The rising interest rates and inflation are pressuring Canadian manufacturing into pursuing even greater operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Talent. Despite talent shortages impacting both manufacturing operations in general and the ICT sector in particular, Canada still boasts the most highly educated workforce among the G7 nations.
3 Examples of Canadian Manufacturers Embracing Industry 4.0
Across the country, companies transform their operations with cutting-edge simulation and digital twin solutions, manufacturing execution systems, and even a coating thickness monitoring technology.
Metal 7
This producer of equipment for iron ore and aluminum industries wanted to double down on its competitive advantage: surface coating. To do so, Metal 7’s coating department implemented cutting-edge digital manufacturing technology to monitor and control the thickness of the applied coating.
The technology allowed Metal 7 to reap two benefits. First, it allowed the company to reduce waste by enabling operators to apply the optimal coating amount. Second, it increased the life span of some parts fivefold as customers could now judge themselves when equipment needed replacing.
CenterLine (Windsor) Limited
This manufacturer of automated welding and assembly lines implemented a simulation and digital twin solution to streamline designing robotic welding, manufacturing, and testing. By ramping up its digital twin capabilities, the manufacturer can now simulate any robot, process, and equipment piece before production.
As a result, CenterLine (Windsor) Limited saw a drastic reduction in project timelines as large job delivery time went down from two years to 50 weeks. Updates requested by customers can also be implemented times faster.
AGS Automotive Systems
This manufacturer of automobile parts leverages a manufacturing execution system (MES) to reduce downtime and improve product quality. What’s more, the MES provides key stakeholders with crucial real-time and historical production data.
The company’s co-president, Joe Loparco, said that the insights derived from this data are a crucial benefit of the MES. They enable workers to pinpoint the root causes of defects and stoppages, resulting in the “a-ha” moments that boost productivity and reduce costs.
4 Industry 4.0 Software Solutions Transforming Manufacturing in Canada
While there’s no one-size-fits-all approach for reaping the benefits of Industry 4.0, these four software solutions are a good place to start.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
A top example of software modernization in manufacturing, an ERP system is the highest-level management system for a business. It brings all business operations to one place, from finance and HR to manufacturing and project management. Think of it as the ultimate centralized system for overseeing the totality of your company’s operations.
ERP systems usually include the following modules:
Finance and accounting
Procurement
Manufacturing
Sales
Customer relationship management
Human resources management
The key benefit of an ERP system is its centralized nature: it serves as the single source of truth for all data pulled from multiple sources and lower-level systems. This enables a bird’s eye view of operations on the enterprise level, which paves the way for process optimization, better collaboration, and real-time insights.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
An MES allows you to monitor and control manufacturing processes on the factory floor. Its key features include:
Data capture for multiple sources (IoT sensors, operators, machines, etc.) to monitor production in real time
Production scheduling based on order priority, available resources, staffing, and equipment capacity
Work order management, including order assignment, instructions, and specifications
Machine and equipment integration to monitor equipment status and collect data
Quality management, including test results, inspections, and measurement monitoring
Material and inventory tracking and management throughout production
Data analytics, visualization, and reporting on key performance metrics
Integrations with other systems (ERP, PLM, etc.)
An MES allows you to identify and eliminate bottlenecks from manufacturing processes, therefore reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Software
A PLM system enables you to manage all data and processes related to a specific product or service throughout its lifecycle across locations and supply chains. Here are its benefits:
All product and process data in one place
Facilitated collaboration across functions
Improved automation capabilities
Data-driven decision-making
Enhanced innovation capabilities
A PLM system’s features usually include:
Change process management
Visual product collaboration
Bill of materials management
Configuration management
MCAD, ECAD, and simulation tools
Product requirements management
A PLM system can also include digital twins of physical assets. They allow for running simulations before making any changes to the actual product, equipment, or process. Digital twins enable you to run cost-benefit analyses on modifications, simulate product changes, or even prevent downtime.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems
A SCADA system, as you can guess from its name, monitors and controls data acquisition processes. It combines both software and hardware to collect data from industrial equipment in real time. It also provides operators with a user interface to manage and monitor industrial processes.
Implementing a SCADA system comes with several key benefits:
A unified view of all industrial processes in a single UI
Real-time monitoring of metrics across the plant, from environmental conditions to product quality
Greater flexibility and responsiveness thanks to remote process control capabilities
Improved efficiency and productivity via task scheduling and script execution
4 Benefits of Industry 4.0 Adoption
In 2024, 76% of Canadian manufacturers experienced a benefit from technology upgrades. However, the top perceived benefits of Industry 4.0 solutions have changed in 2024.
In previous years, the increased throughput and product quality ranked higher. The 2024 survey, however, put the lower operational costs and reduced downtime above those two perks.
Cost Savings
37% of Canadian manufacturers reported lower operational costs following technology upgrades. They can be a result of reduced staff requirements thanks to automation, downtime avoided with predictive maintenance, and increased operational efficiency.
Reduced Downtime
This benefit came in as a close second, with 36% of Canadian manufacturers reporting it in 2024. Industry 4.0 technologies that target this particular goal include ML-powered predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and digital twins.
Increased Operational Efficiency
A rise in throughput is the number three cited benefit of advanced manufacturing solutions. Robotic process automation, collaborative robots, and data-driven process optimization are common ways to reap this benefit.
Improved Quality
29% of Canadian manufacturers reported an improvement in product quality. This can be due to data-driven process improvements, digital twin simulations, and automated defect detection powered by computer vision, among others.
7 Steps to Successfully Implementing Industry 4.0 Solutions
Envisioning an Industry 4.0 project? Here are the seven steps to making your transformation a success.
Understand Where You Stand with Technology
What is your current level of digital maturity? Are there any silos that may undermine the benefits of a cutting-edge solution? These are the questions you should be asking before you can assess what it’ll take to get to point B in your project.
When analyzing your current state, pay attention to:
Available resources
Information systems
Organizational structure
Culture
Readiness across functions (development, production, logistics, marketing/sales)
Current operating model (COM)
You may need a fresh perspective to identify what works and what needs improvement in your organization’s digital systems. In this case, consider hiring an IT consultant.
Zero in on Your Vision
What do you want to achieve with your Industry 4.0 project? Outline the objectives and desired outcomes, ensure they align with strategic goals, and design a target operating model (TOM). Set the key performance indicators and use Canada’s manufacturing industry benchmarks that you’ll use to track your progress later on.
Conduct a Gap Analysis
Now that you have a clear view of points A and B, what will it take for you to make the journey? Consider your resources, especially your in-house talent, as well as your culture, present systems, data capabilities, and cybersecurity.
If you don’t have the right expertise to implement your Industry 4.0 project, you’ll need to partner up with an external vendor. We have a whole guide on finding dedicated developers in Canada to help you out.
Secure Buy-In Across the Organization
Becoming an Industry 4.0 business is impossible without collaboration and communication across the whole organization, from the shop floor to the top management. So, identify key internal stakeholders for your project, seek out their feedback, and ensure they’re on board with your initiative.
Capitalize on Government Support & Incentives
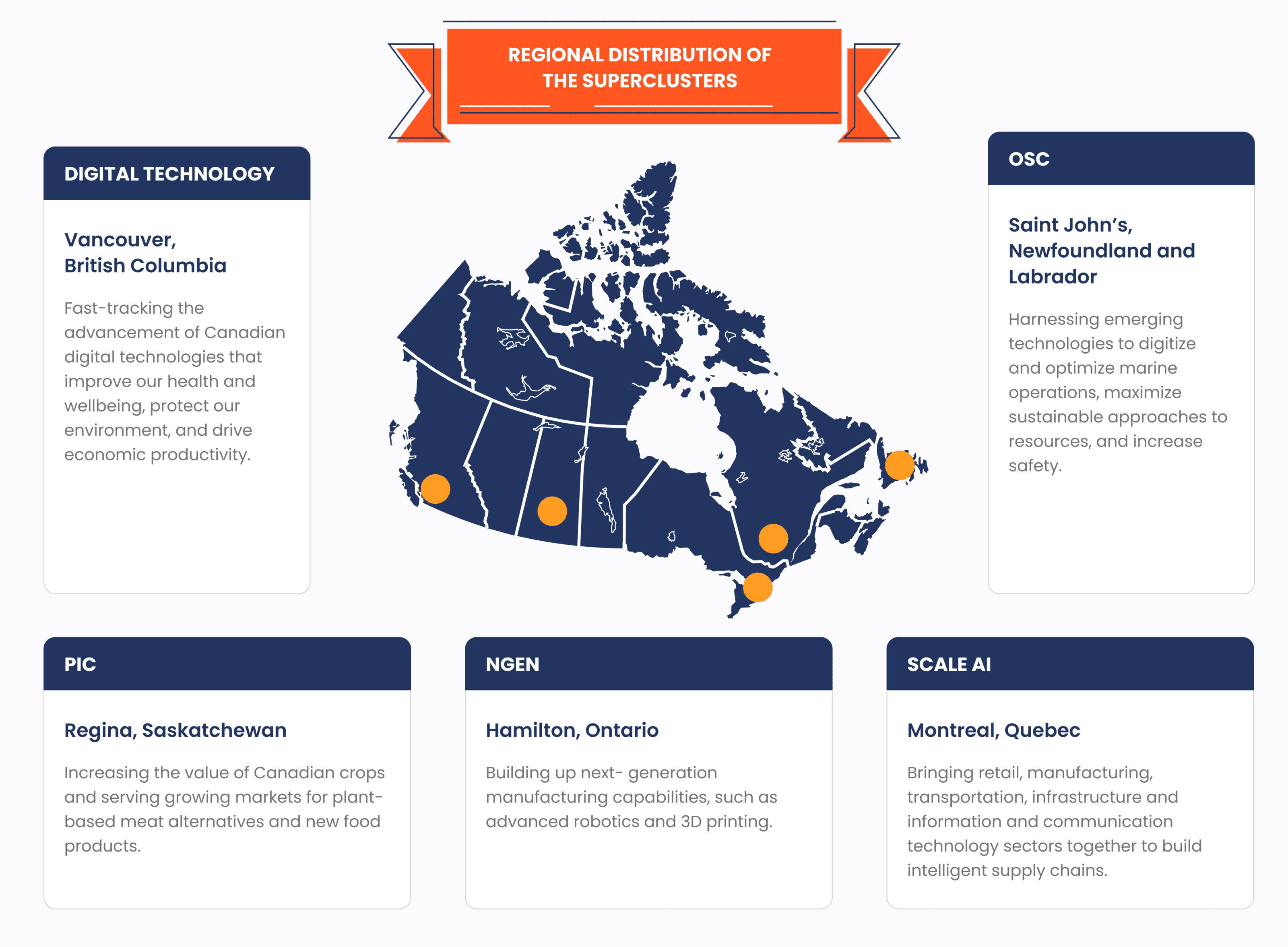
While funding is likely to come primarily from within your organization, you can also benefit from the Canadian government’s incentives. For instance, the government established several Innovation Superclusters that can provide funding and other support to Canadian manufacturers looking to revamp their operations with cutting-edge technologies.
Start with the Right Business Case
Identify a business case that’ll serve as your pilot project/proof of concept. A good starting business case allows you to secure a quick win with a relatively low investment.
Adopt an agile approach to every business case: focus on incremental improvements to the solution. In other words, develop the prototype, test it in a real-world setting, identify what works and what doesn’t, and improve the solution. Rinse and repeat.
Manage Change
Make sure your processes and staff are prepared for the changes that your initiative will bring forth. Invest in training, adapt workflows to make them more efficient, and remove potential roadblocks across functions.
If you don’t have a change management strategy in place, now is the time to devise one. It’ll ensure everyone is on the same page regarding changes in processes, digital tools, and workflows.
Case Study: Turning an ERP System into a Competitive Advantage
In 2014, Cam Tran, an oil-filled distribution transformer manufacturer, reached out to Integrio Systems with a request to develop a work instruction management system. This system would bring all standardized work instructions to one place, serving as a single source of truth. It would also facilitate organizing, finding, editing, and controlling instructions.
We created Jive, which served as a pilot project for a larger system that optimized the manufacturer’s business processes. Deemed a success, Jive evolved into a comprehensive ERP system with the following functionality:
Production and inventory management
Project management
Document storage and management
Production volume and financial results forecasting
Winding schedule optimization
Quality control
Internal audits
Ready to reap the benefits of Industry 4.0 solutions? We can help you reduce costs, improve product quality, and boost throughput with a custom manufacturing application tailored to your needs. Let’s discuss how our expertise can help you remain competitive.
Contact us

