AI in Cybersecurity: Protecting Against Tomorrow’s Threats

Data breaches, ransomware attacks, identity theft... Just several threats that can ruin your company’s reputation and processes. Traditional security measures, while essential, often struggle to keep up with the rapidly evolving tactics of cybercriminals.
That’s exactly when AI in cybersecurity is necessary. With advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities, it provides such protection that traditional methods can hardly match. In fact, 47% of businesses improved their security after adopting AI.
In this post, we’ll discuss how artificial intelligence enhances your security posture and which threats it can help you mitigate.
Importance of AI in Cybersecurity
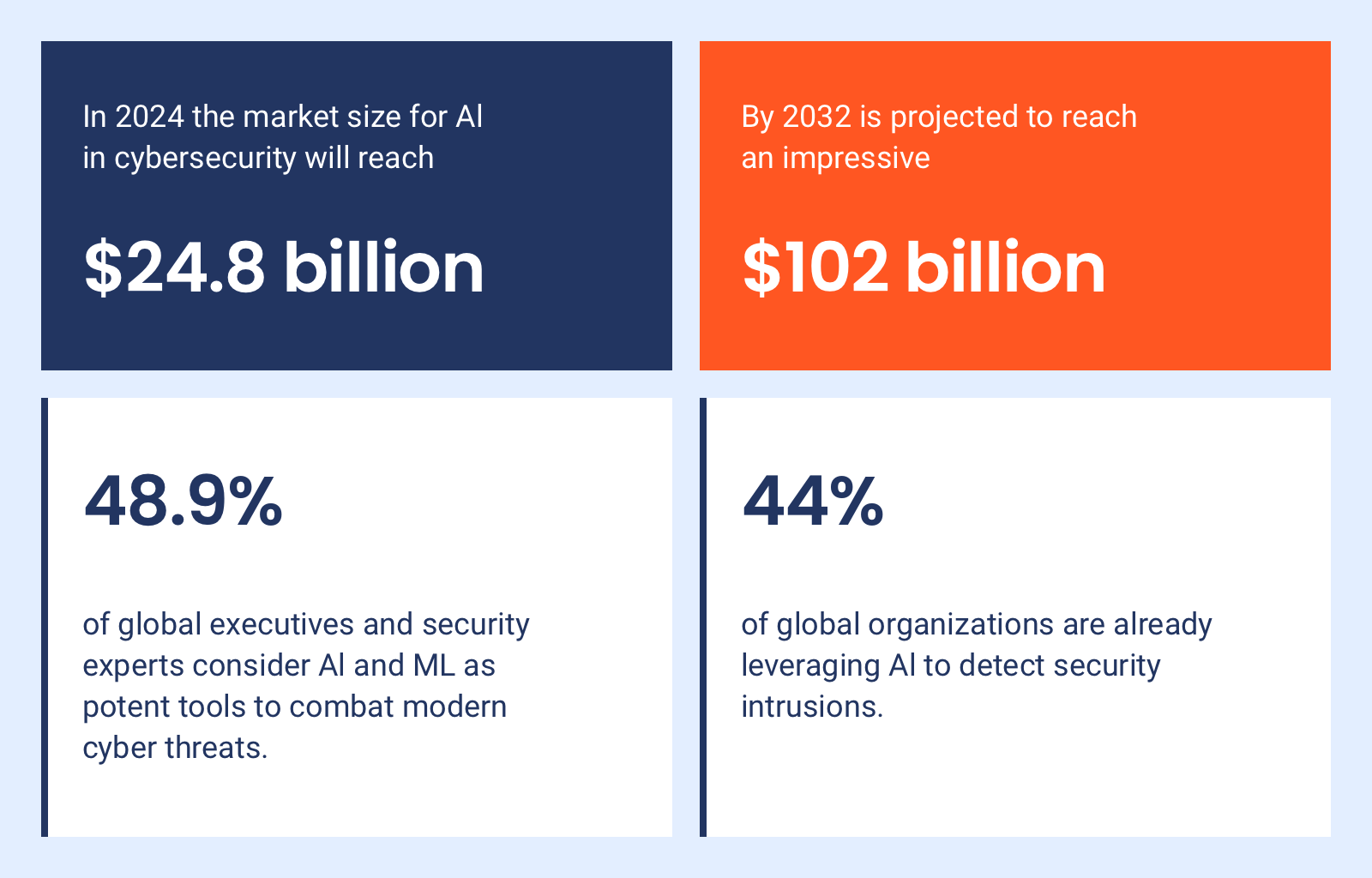
In short, AI is not just an add-on — it’s a fundamental part of the modern cybersecurity toolkit. The growing market confirms this: valued at $24.3 billion in 2023, AI cybersecurity is expected to reach nearly $102 billion by 2032.
But why is AI important for cybersecurity?
For starters, AI can handle massive amounts of data at lightning speed, something human cybersecurity analysts often can’t cope with. No wonder 69% of enterprises believe that AI is a must-have for tackling the growing number of cyber threats. With the complexity and frequency of attacks increasing, counting solely on human resources isn’t enough anymore.
Not by data analytics alone, but AI is also improving cybersecurity through advanced threat detection. This is why we’re seeing more investments in this tech. The banking sector, a major hacker’s target, alone accounted for 13.4% of the $154 billion spent on AI globally in 2023.
From a regional perspective, North America leads the game. In 2021, it made up 38.3% of the total revenue in artificial intelligence in cybersecurity and keeps being at the forefront of this technology.
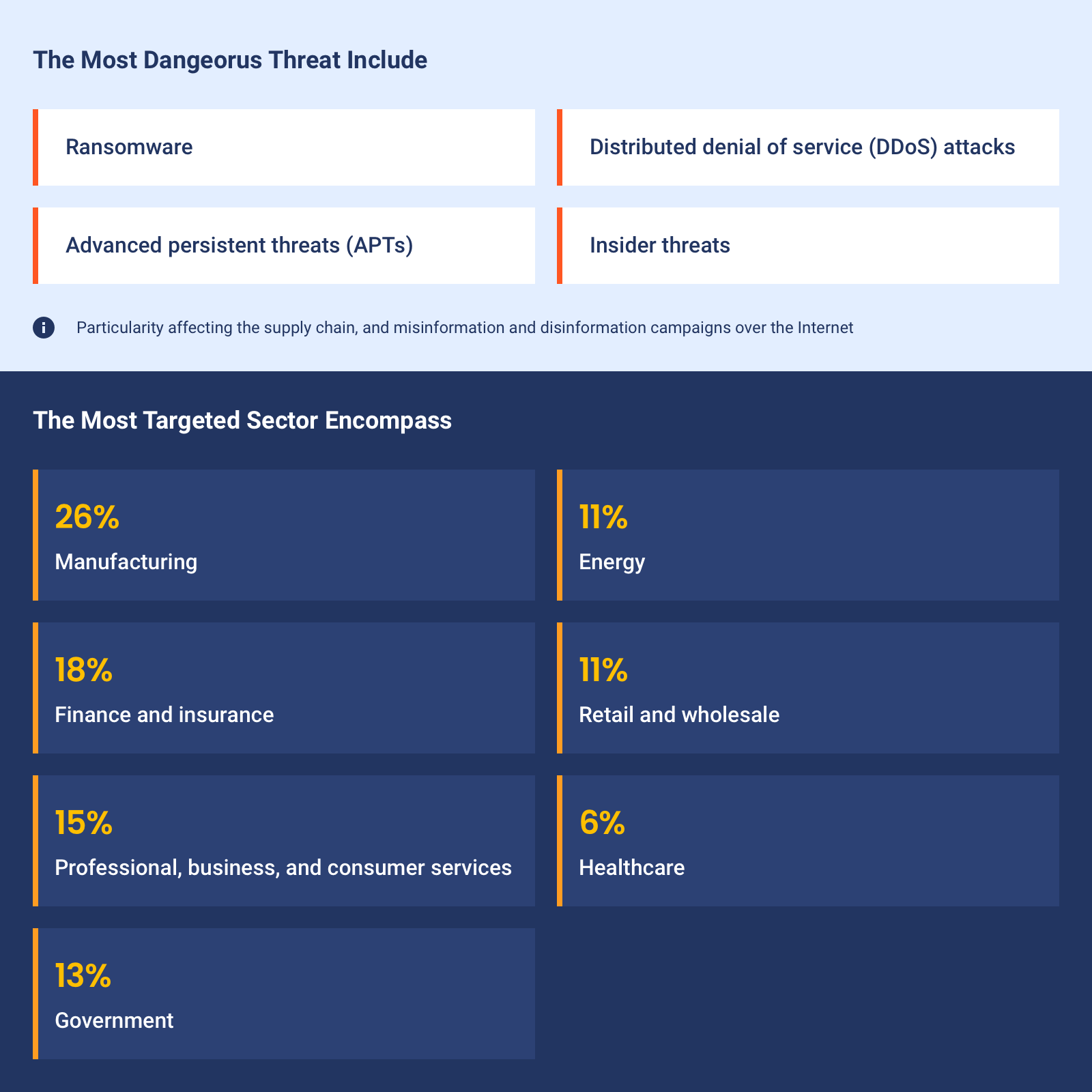
Most Dangerous Threats and Targeted Sectors
Knowing the possible dangers is the first step to strengthening your defenses. Let’s explore some of the most harmful threats out there and the industries they target.
Here are the threats to be aware of:
Ransomware. It’s a type of malicious software cybercriminals use to lock up your computer systems and demand a ransom to unlock them. Once it infects the system, ransomware encrypts your files, making them inaccessible. Retrieving data is only possible through the decryption key.
Advanced persistent threats (APTs). These are highly sophisticated attacks, often carried out by nation-states or organized crime groups. They can lie dormant in your system for months or even years, stealing data, disrupting operations, and causing substantial damage — mostly for political or economic reasons.
Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. Imagine a million people trying to call your phone all at once. That’s basically a DDoS attack. It overwhelms your system with traffic, making it inaccessible to legitimate users.
Insider threats. Sometimes, the most dangerous threat comes from within. Employees, contractors, or partners with authorized access can maliciously or unintentionally misuse their privileges and compromise your data or the entire system.
Which industries suffer from these threats the most? According to Statista, the sectors most targeted by cyberattacks in 2023 were:
Manufacturing (26%). Manufacturing companies store sensitive intellectual property, supply chain information, and customer data. Cyberattacks can undermine production and lead to product recalls.
Finance and insurance (18%). Financial institutions are lucrative targets for hackers due to the sensitive data and assets they manage. That’s why they need to implement best practices for secure FinTech development.
Professional, business, and consumer services (15%). This broad category covers everything from law firms and accounting services to consulting and customer support. All of them deal with client data. Therefore, robust protection is necessary.
Energy (11%). Critical infrastructure like power plants can be targeted digitally, potentially leading to disruptions, economic loss, and even physical harm.
Retail and wholesale (11%). Credit card information, customer details, purchase history, and even personal preferences can all be exploited in a data breach. This can ultimately result in reputational damage and significant financial losses.
Healthcare (6%). One of the most vulnerable industries to cyberattacks, healthcare deals with highly sensitive patient data. This sector has also had the highest average data breach cost in recent years, reaching nearly $11 million.
Government (13%). Governments hold a lot of sensitive information — from national security secrets to citizen data. They’re a prime target for espionage and sabotage.
AI-Powered Cybersecurity Solutions
Artificial intelligence is making a difference in cybersecurity owing to the unique capabilities it offers. Let’s go through them in detail.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence (AI), is at the heart of many cybersecurity solutions. It involves training algorithms on large datasets to identify patterns and anomalies. Once trained, these algorithms can automatically detect and respond to potential security threats. In particular, ML is used for:
Anomaly detection. ML models can detect unusual behavior by analyzing network traffic, user activities, and system operations. For example, if a user suddenly starts accessing numerous records with sensitive data, ML can flag this as a potential threat.
Threat prediction. By learning from historical data, ML algorithms can predict what kind of threats might pop up in the future and identify a possible vulnerability before it is exploited.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing enables machines to understand and interpret human language. In cybersecurity, this technology is used to analyze emails, social media posts, and other text-based data to detect phishing attempts, malicious links, and other threats. Here’s how it makes this possible:
Phishing detection. NLP can identify suspicious language patterns and keywords commonly used in phishing scams.
Threat intelligence. NLP can learn from threat intelligence data like news articles, blogs, and forums to help identify and address threats and vulnerabilities.
Sentiment analysis. The capability to analyze the tone and context of communications lets NLP identify insider threats or social engineering attacks.
AI Algorithms for Real-Time Monitoring and Response
Real-time monitoring and response algorithms are critical for cyberattack prevention and handling. With these AI tools, you can keep an eye on your system around the clock for any suspicious activity. If something unusual happens, the algorithm can automatically shut down affected systems, block suspicious IP addresses or alert your security team right away. This means you can save precious time while reacting to a threat.
Successful Use Cases of AI in Cyber Security
Numerous organizations have successfully deployed AI-powered cybersecurity solutions. Here are just several examples:
Advanced threat detection. Vectra AI, a cybersecurity firm, provides tools that help find and counteract unauthorized activities quickly. In particular, it ensures AI security for telecommunications companies.
Emerging threat protection. Wells Fargo, a US-based financial services company, has adopted a multi-layered cybersecurity strategy for addressing both current and future threats. Their approach combines AI-enhanced threat intelligence, rigorous monitoring, and incident response programs, along with traditional tools like firewalls, antiviruses, and endpoint protection.
Vulnerability management. Splunk, a monitoring software provider, offers AI-powered tools for vulnerability assessment and management. It also allows users to quickly detect and respond to incidents, making their security efforts more efficient.
Fraud detection. PayPal, an online payment system, uses AI to detect fraudulent activity patterns. By analyzing vast amounts of transaction data, the company can identify suspicious behavior, for example, if someone attempts to use your stolen card.
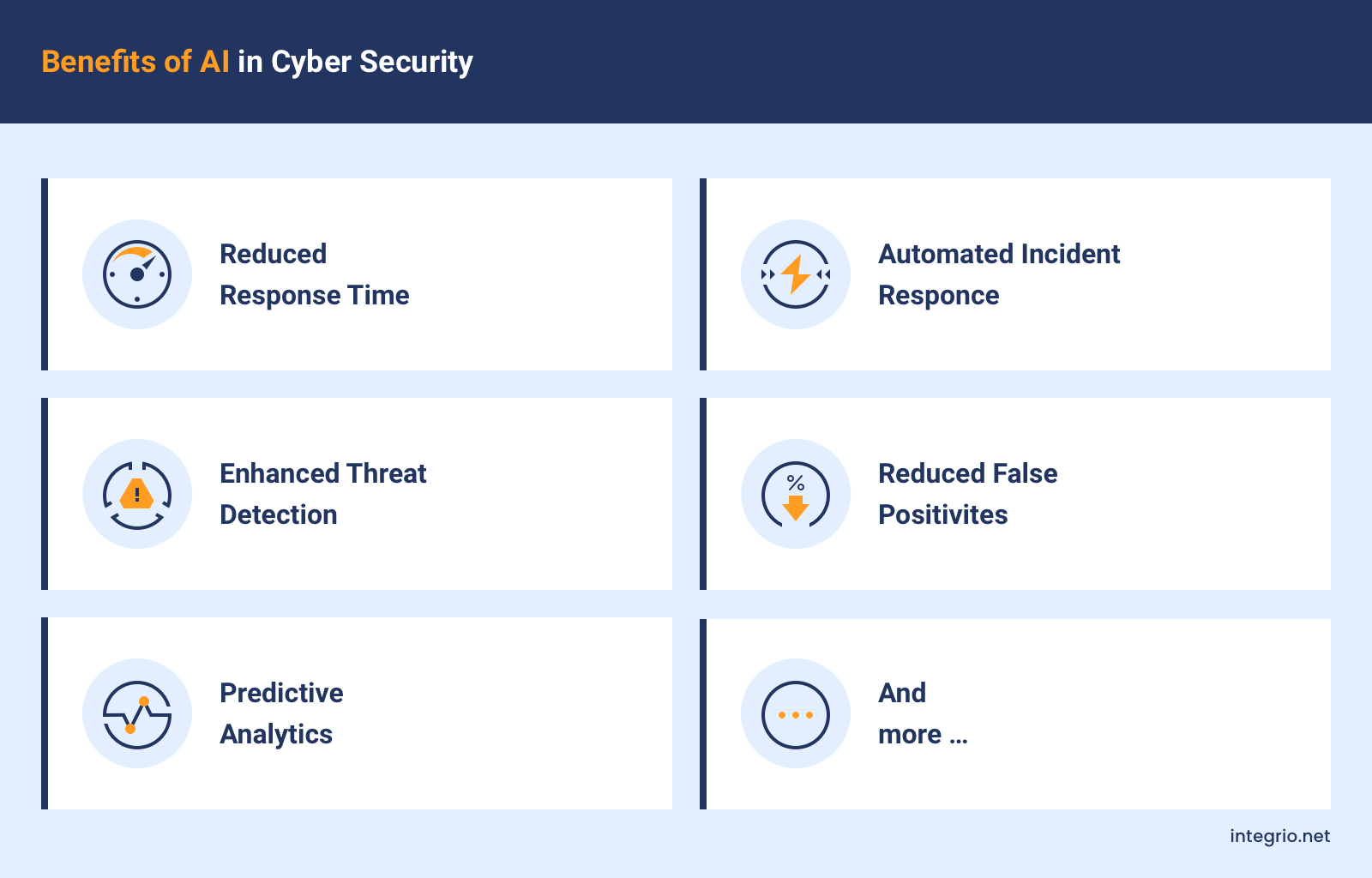
Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
Let’s recap the importance of AI in cybersecurity by looking at the most compelling benefits this tech offers:
Predictive analytics. With AI-powered predictive analytics, you can anticipate potential threats by analyzing historical data and identifying unusual patterns. This lets you take proactive measures — say, patching vulnerabilities or deploying additional access controls — before an actual attack occurs.
Enhanced threat detection. AI can detect anomalies and suspicious activities that human analysts may overlook. Again, by sifting through vast amounts of data. As a result, this tech helps you identify security breaches early on.
Automated incident response. Incident response requires a lot of effort if handled manually. With AI, you can automate such tasks as isolating compromised systems, containing threats, or applying patches.
Reduced false positives. Traditional security systems often generate plenty of false alerts, which can be a hassle for security teams. AI helps cut down on these false positives by accurately distinguishing between what’s actually suspicious and what’s not.
Reduced response time. AI-powered solutions can spot and respond to threats way faster than humans. They handle routine tasks automatically and provide real-time updates so you can catch and fix security issues quickly.
Conclusion
Using artificial intelligence in cybersecurity is non-negotiable. AI beats traditional methods and human capabilities in predicting, detecting, and responding to security incidents, which makes it a crucial investment for businesses that care for their data, customers, and assets.
If you’re looking to protect your system with AI, our team has the expertise you require. Having provided AI and ML development services for the last two decades, we can keep your organization safe from emerging threats. Don’t wait for a security breach to happen — contact us today to get ahead of the hackers.
Contact us

